Reactive notes
Not starting with the traditional definitions but some quick one-liner notes about the different parts & pieces of the React.
Component in React
1. Defining a Component
- Always name your components with upper case first letter.
2. Types
- Function components
- Class components
3. Ways of holding data
- props
- prop types (runtime prop validation)
- states
- setState (merge previous state & current state)
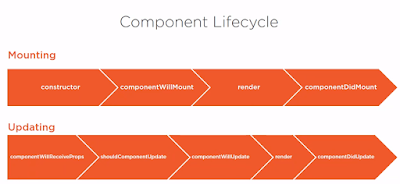
4. Life cycle
Saying: All React components must act like pure functions with respect to their props.
JSX
1. External domain language, to generate html using JS to build a custom react component.
2. Supports html like syntax in JS.
3. Each element is transformed into a javascript function call.
4. Transcript compiler is required to convert into javascript like babel.
5. Props in JSX: <Hello a={10} />
Spread Attributes
ES2015 has introduced spread syntax.
Example: -
function Sum(props){
return <div> {props.a} + {props.b} = {props.a + props.b} </div>
}
const props = {a:1, b:2};
const element = <sum {...props} />
Unescaping Content (Setting innerHtml of the elements)
function Container(props){
return <p innerHtml = {{__html:props.myhtml}}>
}
<Container myhtml="<b>Hello World!</b>" />
Event
Events can be: -
1. DOM events (button click, dom scroll, etc)
2. Component events
Model-View-Intent
Redux
1. Common state container library.
2. Help to implement M-V-I pattern.
3. It reduces the stream of intent to an object.
Redux API
createStore(reducer, initialState)
getState()
dispach()
subscribe()
React Hooks
- Hooks brin state and lifecycle to React functional components.
- hooks are easy to use without complex usage patterns.
Only Call Hooks at the Top Level.
1. useState - used for two-way binding.
3. useEffect - Adding/ Removing DOM listeners
Some react hooks:
1. useContext
2. useReducer
How reducer works?
(previousState, action) => newState
3. useCallback
4. useMemo
Flux API
Important methods in Flux API
Sources:-
https://app.pluralsight.com/paths/skill/react
http://hannesdorfmann.com/android/model-view-intent
Component in React
1. Defining a Component
- Always name your components with upper case first letter.
2. Types
- Function components
- Class components
3. Ways of holding data
- props
- prop types (runtime prop validation)
- states
- setState (merge previous state & current state)
4. Life cycle
Saying: All React components must act like pure functions with respect to their props.
JSX
1. External domain language, to generate html using JS to build a custom react component.
2. Supports html like syntax in JS.
3. Each element is transformed into a javascript function call.
4. Transcript compiler is required to convert into javascript like babel.
5. Props in JSX: <Hello a={10} />
Naming JSX components:
Spread Attributes
ES2015 has introduced spread syntax.
Example: -
function Sum(props){
return <div> {props.a} + {props.b} = {props.a + props.b} </div>
}
const element = <sum {...props} />
Unescaping Content (Setting innerHtml of the elements)
function Container(props){
return <p innerHtml = {{__html:props.myhtml}}>
}
<Container myhtml="<b>Hello World!</b>" />
Event
Events can be: -
1. DOM events (button click, dom scroll, etc)
2. Component events
Model-View-Intent
1. Common state container library.
2. Help to implement M-V-I pattern.
3. It reduces the stream of intent to an object.
Redux API
createStore(reducer, initialState)
getState()
dispach()
subscribe()
React Hooks
- Hooks brin state and lifecycle to React functional components.
- hooks are easy to use without complex usage patterns.
Only Call Hooks at the Top Level.
1. useState - used for two-way binding.
2. useRef - Primarily used to allow access directly to an element in the dom.import React, {useState} from 'react';
const InputElement = () => {
const [inputText, setInputText] = useState("");const [historyList, setHistoryList] = useState([]);
return <div><inputonChange={(e) => {setInputText(e.target.value);setHistoryList([...historyList, e.target.value]);}}placeholder="Enter Some Text"></input><br/>{inputText}<ul>{historyList.map((rec) => {return <div>{rec}</div>;})}</ul></div>};
export default InputElement;
import React, {useRef} from 'react';
const ImageTogglerOnMouseOver = ({primaryImg, secondaryImg}) => {
const imageRef = useRef(null);
return (
<img
onMouseOver = {() => {
imageRef.current.src = secondaryImg;
}}
onMouseOut = {() => {
imageRef.current.src = primaryImg;
}}
src = {primaryImg}
alt = "" ref = {imageRef}
/>
);
};
export default ImageTogglerOnMouseOver;
3. useEffect - Adding/ Removing DOM listeners
import React, {useEffect} from 'react';
const syntax = () => {
const [checkBoxValue, setCheckBoxValue] = useState(false);
useEffect(() => {
console.log('in useEffect');
return ()=> {
console.log('in useEffect cleanup');
};
}, [checkBoxValue]);
return(
<div></div>
);
};
export default syntax;
Some react hooks:
1. useContext
2. useReducer
How reducer works?
(previousState, action) => newState
3. useCallback
4. useMemo
Flux API
Important methods in Flux API
Redux Setup
Sources:-
https://app.pluralsight.com/paths/skill/react
http://hannesdorfmann.com/android/model-view-intent








Comments